How to Test Android Apps with Appium: Setup Guide + 17 Troubleshooting Fixes

Introduction to Appium Android Testing
Manual testing doesn't scale. Testing an Android app across 12 versions, 50 device models, and hundreds of user flows manually is impractical. Bugs slip through–transfers fail on Android 11 but work on Android 13, apps crash during screen rotation, balances show incorrect after failed retries.
Appium Android testing solves this. Write tests once, run them across multiple Android versions, device sizes, and configurations. This Android testing tutorial covers complete Appium setup, writing your first automated test with WebDriverIO, and fixing 17 common problems you'll encounter.
What is Appium and Why Use It for Android Testing?
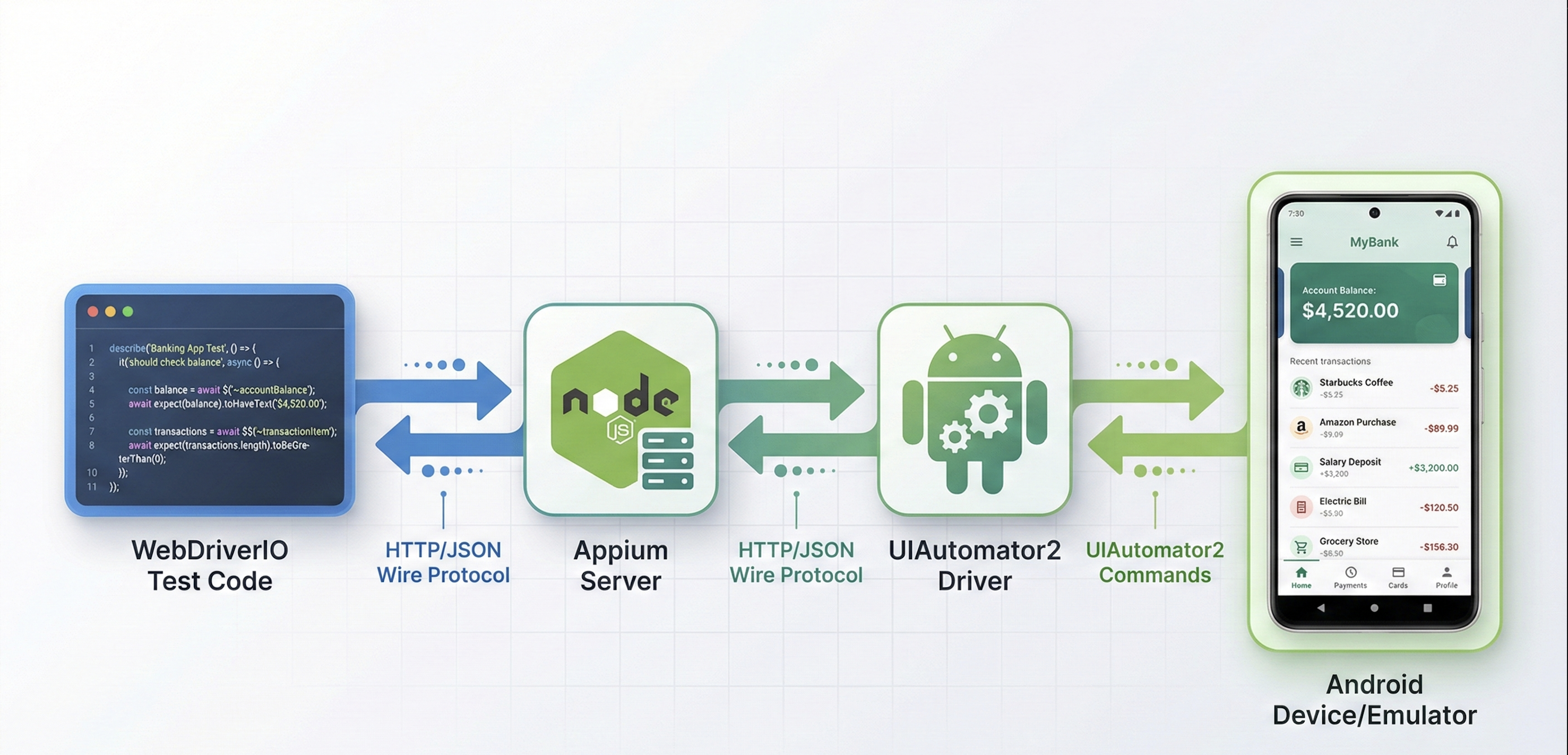
Appium is an open-source test automation framework for mobile applications. It works with native Android apps, iOS apps, hybrid apps, and mobile web browsers using the WebDriver protocol–the same standard that powers Selenium for web testing.
For Android UI testing specifically, Appium leverages the UIAutomator2 driver–Google's official Android automation framework. This means your Android test scripts interact with apps the same way users do, providing reliable mobile app quality assurance.
Appium doesn't require modifying your app's source code. You test the same APK that ships to production. It supports multiple programming languages (JavaScript, Python, Java, Ruby, C#) and runs tests on real devices and emulators.
When your test says "tap the login button," Appium translates that into UIAutomator2 commands that Android understands. The app responds as if a real user tapped the screen.
Appium's cross-platform capability matters when testing both Android and iOS. Write your test logic once, configure different drivers for each platform, reuse most of your code. For a deeper comparison of testing frameworks, see our guide on Test Automation Frameworks: Playwright, Selenium, Cypress, and Appium Compared.
Appium Android Testing: Prerequisites and System Requirements
Before installing Appium, you need four core dependencies: Java JDK, Node.js, Android SDK, and the Appium server.
System Requirements:
- macOS 10.14+, Windows 10+, or Linux (Ubuntu 18.04+)
- 8GB RAM minimum (16GB recommended for running emulators)
- 20GB free disk space
Verify what you have installed:
# Check Java version (need JDK 8 or higher)
java -version
# Check Node.js version (need 14+ recommended)
node --version
# Check npm version
npm --version
# Check if adb is installed
adb versionIf any command fails, install that dependency in the following sections.
Installing Java JDK for Appium Android Setup
macOS:
# Install via Homebrew
brew install openjdk@11
# Add to PATH
echo 'export PATH="/usr/local/opt/openjdk@11/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.zshrc
source ~/.zshrcWindows:
- Download JDK installer from Oracle's website
- Run installer and note installation path (e.g.,
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11) - Add to system PATH:
- Open System Properties → Environment Variables
- Add new system variable:
JAVA_HOME=C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11 - Edit PATH variable, add:
%JAVA_HOME%\bin
Linux (Ubuntu):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdk
# Verify installation
java -versionNode.js and npm Installation for Appium Mobile Automation
macOS:
# Install via Homebrew
brew install node
# Verify
node --version
npm --versionWindows:
Download the Node.js installer from nodejs.org and run it. The installer includes npm automatically.
Linux:
# Using NodeSource repository
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_18.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
# Verify
node --version
npm --versionInstalling Android SDK and Android Studio
Android Studio includes the Android SDK and tools for creating virtual devices.
- Download Android Studio from developer.android.com/studio
- Run the installer and follow the setup wizard
- During setup, ensure "Android SDK" and "Android Virtual Device" are checked
After installation, open Android Studio:
Configure SDK:
- Go to Settings/Preferences → Appearance & Behavior → System Settings → Android SDK
- Under SDK Platforms, install at least one Android version (Android 13/API 33 recommended)
- Under SDK Tools, ensure these are installed:
- Android SDK Build-Tools
- Android SDK Platform-Tools
- Android Emulator
- Intel x86 Emulator Accelerator (HAXM) on Intel Macs/Windows
Set environment variables:
macOS/Linux - Add to ~/.zshrc or ~/.bashrc:
export ANDROID_HOME=$HOME/Library/Android/sdk # macOS
# export ANDROID_HOME=$HOME/Android/Sdk # Linux
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/emulator
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/tools
export PATH=$PATH:$ANDROID_HOME/tools/binThen reload your shell:
source ~/.zshrc # or source ~/.bashrcWindows - Add system environment variables:
- Open System Properties → Environment Variables
- Add new system variable:
- Name:
ANDROID_HOME - Value:
C:\Users\YourUsername\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk
- Name:
- Edit PATH, add these entries:
-
%ANDROID_HOME%\platform-tools -
%ANDROID_HOME%\emulator -
%ANDROID_HOME%\tools -
%ANDROID_HOME%\tools\bin
-
Verify the installation:
adb version
# Should output: Android Debug Bridge version X.X.X
echo $ANDROID_HOME # macOS/Linux
echo %ANDROID_HOME% # Windows
# Should output your SDK pathAndroid Emulator Setup: Creating AVD for Appium Testing
You need an Android emulator to run your tests.
In Android Studio:
- Open AVD Manager (Tools → Device Manager)
- Click "Create Device"
- Select a device definition (Pixel 5 recommended for testing)
- Select a system image (download Android 13/API 33 if not already available)
- Name it "AppiumTest" for easy reference
- Click Finish
Start the emulator from command line:
# List available AVDs
emulator -list-avds
# Start your AVD
emulator -avd AppiumTestWait for the emulator to fully boot (you'll see the Android home screen). Verify adb can see it:
adb devices
# Should output:
# List of devices attached
# emulator-5554 deviceThe device name (like emulator-5554) is what Appium will use to connect.
Installing Appium Server
Install Appium globally via npm:
npm install -g appium
# Verify installation
appium --version
# Should output something like: 2.2.1Appium 2.x requires installing drivers separately. Install the UIAutomator2 driver for Android:
appium driver install uiautomator2
# Verify driver installation
appium driver list
# Should show uiautomator2@X.X.X installedStart the Appium server to verify everything works:
appiumYou should see output like:
[Appium] Welcome to Appium v2.2.1
[Appium] Appium REST http interface listener started on http://0.0.0.0:4723
[Appium] Available drivers:
[Appium] - uiautomator2@2.34.1 (automationName 'UiAutomator2')
Leave this terminal window running. Appium server needs to be active when you run tests.
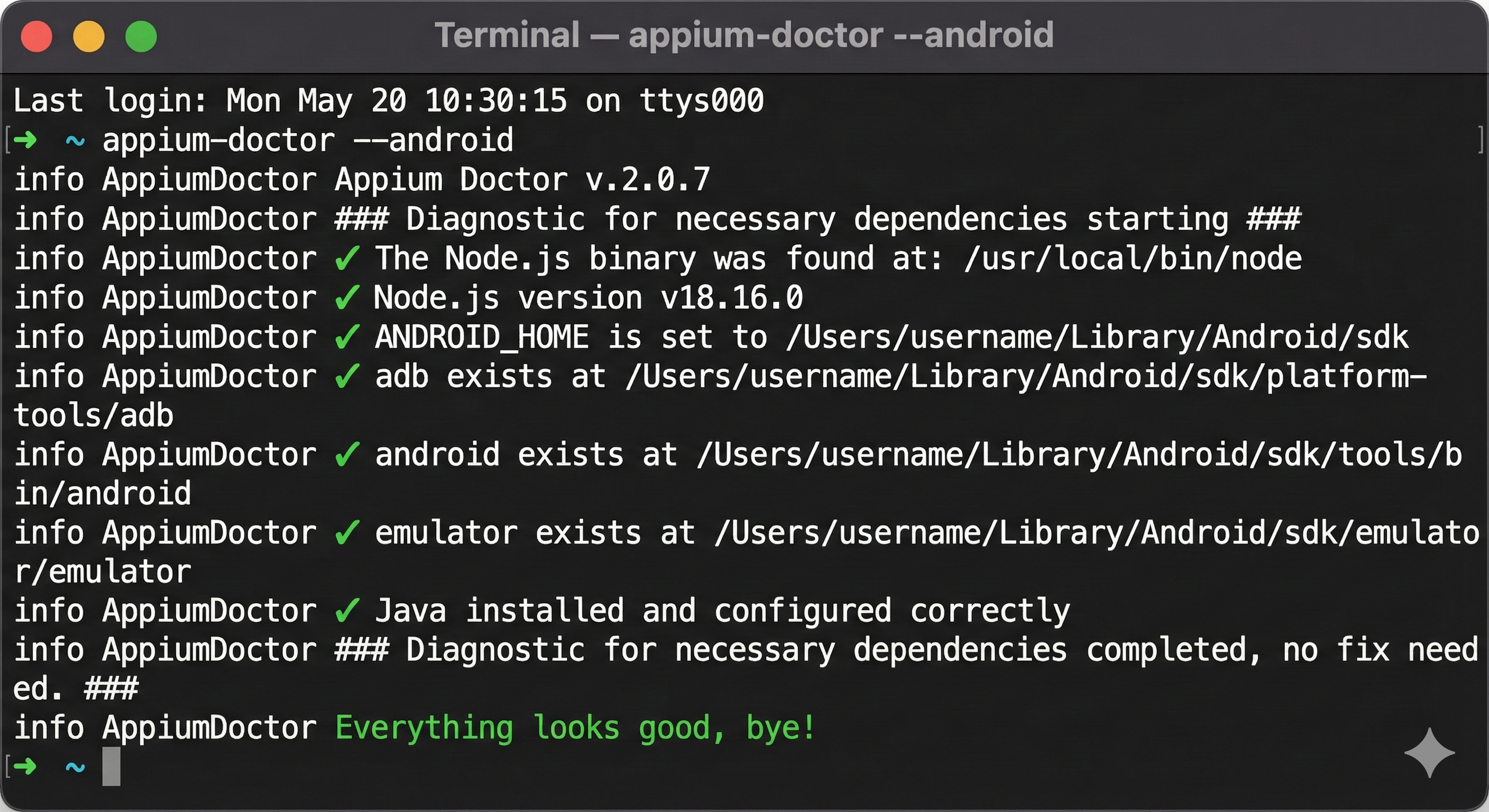
Installing Appium Doctor (Optional but Recommended)
Appium Doctor checks if your environment is configured correctly:
npm install -g appium-doctor
# Run diagnostics
appium-doctor --androidThis command checks for Java, Android SDK, environment variables, and other dependencies. Fix any issues it reports before proceeding.
Setting Up Your Test Project with WebDriverIO
Create a new directory for your tests:
mkdir appium-android-test
cd appium-android-test
npm init -yInstall WebDriverIO and Appium dependencies:
npm install --save-dev @wdio/cli
npm install --save-dev @wdio/local-runner
npm install --save-dev @wdio/mocha-framework
npm install --save-dev @wdio/spec-reporter
npm install --save-dev @wdio/appium-serviceInitialize WebDriverIO configuration:
npx wdio configWhen prompted:
- Test environment: Mobile - native/hybrid apps
- Backend: On my local machine
- Framework: Mocha
- Specs location: ./test/specs//*.js** (default)
- Reporter: spec
- Services: appium (select this)
- Base URL: Leave empty (not needed for mobile)
This creates wdio.conf.js in your project root.
Configuring WebDriverIO for Android
Edit wdio.conf.js and configure the capabilities for Android:
exports.config = {
runner: 'local',
port: 4723,
specs: [
'./test/specs/**/*.js'
],
capabilities: [{
platformName: 'Android',
'appium:automationName': 'UiAutomator2',
'appium:deviceName': 'AppiumTest', // Your AVD name
'appium:platformVersion': '13.0', // Your Android version
'appium:app': '/path/to/your/app.apk', // Path to your APK
'appium:appWaitActivity': 'com.yourapp.MainActivity',
'appium:noReset': false, // Uninstall app after session
'appium:newCommandTimeout': 240
}],
logLevel: 'info',
bail: 0,
waitforTimeout: 10000,
connectionRetryTimeout: 120000,
connectionRetryCount: 3,
services: ['appium'],
framework: 'mocha',
reporters: ['spec'],
mochaOpts: {
ui: 'bdd',
timeout: 60000
}
}Key capabilities explained:
platformName: The mobile OS (Android or iOS)automationName: UIAutomator2 for AndroiddeviceName: Name of your emulator or real deviceplatformVersion: Android version (e.g., 13.0)app: Absolute path to your APK fileappWaitActivity: Main activity Appium should wait for after app launchnoReset: If true, keeps app data between sessionsnewCommandTimeout: Seconds before Appium times out waiting for a command
Android App Configuration: Package Names for Appium Tests
You need to know your app's package name and main activity for configuration. Extract this from your APK:
# Using aapt (Android Asset Packaging Tool)
aapt dump badging /path/to/your/app.apk | grep package
# Output: package: name='com.yourcompany.yourapp' versionCode='1'
# Find launchable activity
aapt dump badging /path/to/your/app.apk | grep launchable-activity
# Output: launchable-activity: name='com.yourcompany.yourapp.MainActivity'Alternatively, if you don't have the APK source:
# Install app on emulator/device first
adb install /path/to/your/app.apk
# Get package name of installed apps
adb shell pm list packages | grep yourapp
# Get main activity
adb shell dumpsys package com.yourcompany.yourapp | grep -A 1 MAINWriting Your First Appium Android Test
Let's test a simple fintech app login flow. Create test/specs/login.spec.js:
describe('Fintech App Login Test', () => {
it('should successfully log in with valid credentials', async () => {
// Wait for app to load
await driver.pause(3000);
// Find and fill email field
const emailField = await $('~email-input'); // Using accessibility ID
await emailField.setValue('user@example.com');
// Find and fill password field
const passwordField = await $('~password-input');
await passwordField.setValue('SecurePass123!');
// Tap login button
const loginButton = await $('~login-button');
await loginButton.click();
// Wait for home screen to load
await driver.pause(2000);
// Verify we're on home screen by checking for balance element
const balanceLabel = await $('~account-balance');
const isDisplayed = await balanceLabel.isDisplayed();
// Assert that we successfully logged in
expect(isDisplayed).toBe(true);
});
it('should show error message for invalid credentials', async () => {
// Find and fill email field
const emailField = await $('~email-input');
await emailField.setValue('invalid@example.com');
// Find and fill password field
const passwordField = await $('~password-input');
await passwordField.setValue('WrongPassword');
// Tap login button
const loginButton = await $('~login-button');
await loginButton.click();
// Wait for error message
await driver.pause(1000);
// Find error message
const errorMessage = await $('//*[@text="Invalid email or password"]');
const errorDisplayed = await errorMessage.isDisplayed();
expect(errorDisplayed).toBe(true);
});
});Run the test:
# Make sure Appium server is running in another terminal
# appium
# Run the test
npx wdio run wdio.conf.jsYou should see output like:
[Android 13.0 #0-0] Running: Android 13.0 on AppiumTest
[Android 13.0 #0-0] Session ID: 4a2e7f1b-3c8d-4e2f-9a1b-5c3d2e1f0a9b
[Android 13.0 #0-0]
[Android 13.0 #0-0] Fintech App Login Test
[Android 13.0 #0-0] ✓ should successfully log in with valid credentials
[Android 13.0 #0-0] ✓ should show error message for invalid credentials
[Android 13.0 #0-0]
[Android 13.0 #0-0] 2 passing (15.3s)
Finding Elements in Android Apps with Appium Selectors
Element location is critical for test reliability. Appium provides multiple strategies for finding elements.
Using Accessibility ID (Recommended)
The most reliable strategy. Use the content-desc attribute in Android:
// In your Android app XML:
// <Button android:contentDescription="login-button" />
const loginButton = await $('~login-button');
await loginButton.click();Using XPath
Flexible but slower and more brittle:
// Find by text
const element = await $('//*[@text="Transfer Money"]');
// Find by resource-id
const element = await $('//*[@resource-id="com.app:id/transfer_button"]');
// Find by class and text
const element = await $('//android.widget.Button[@text="Submit"]');
// Find by index
const firstButton = await $('(//android.widget.Button)[1]');Using UIAutomator Selector (Android-specific)
Most powerful for Android:
// Find by text
const element = await $('android=new UiSelector().text("Transfer")');
// Find by text contains
const element = await $('android=new UiSelector().textContains("Trans")');
// Find by resource ID
const element = await $('android=new UiSelector().resourceId("com.app:id/button")');
// Find by class name
const element = await $('android=new UiSelector().className("android.widget.Button")');
// Combining selectors
const element = await $('android=new UiSelector().className("android.widget.EditText").instance(0)');Using Resource ID
Direct and reliable when available:
const element = await $('id=com.app:id/transfer_button');Android App Inspection: Finding Test Automation Selectors
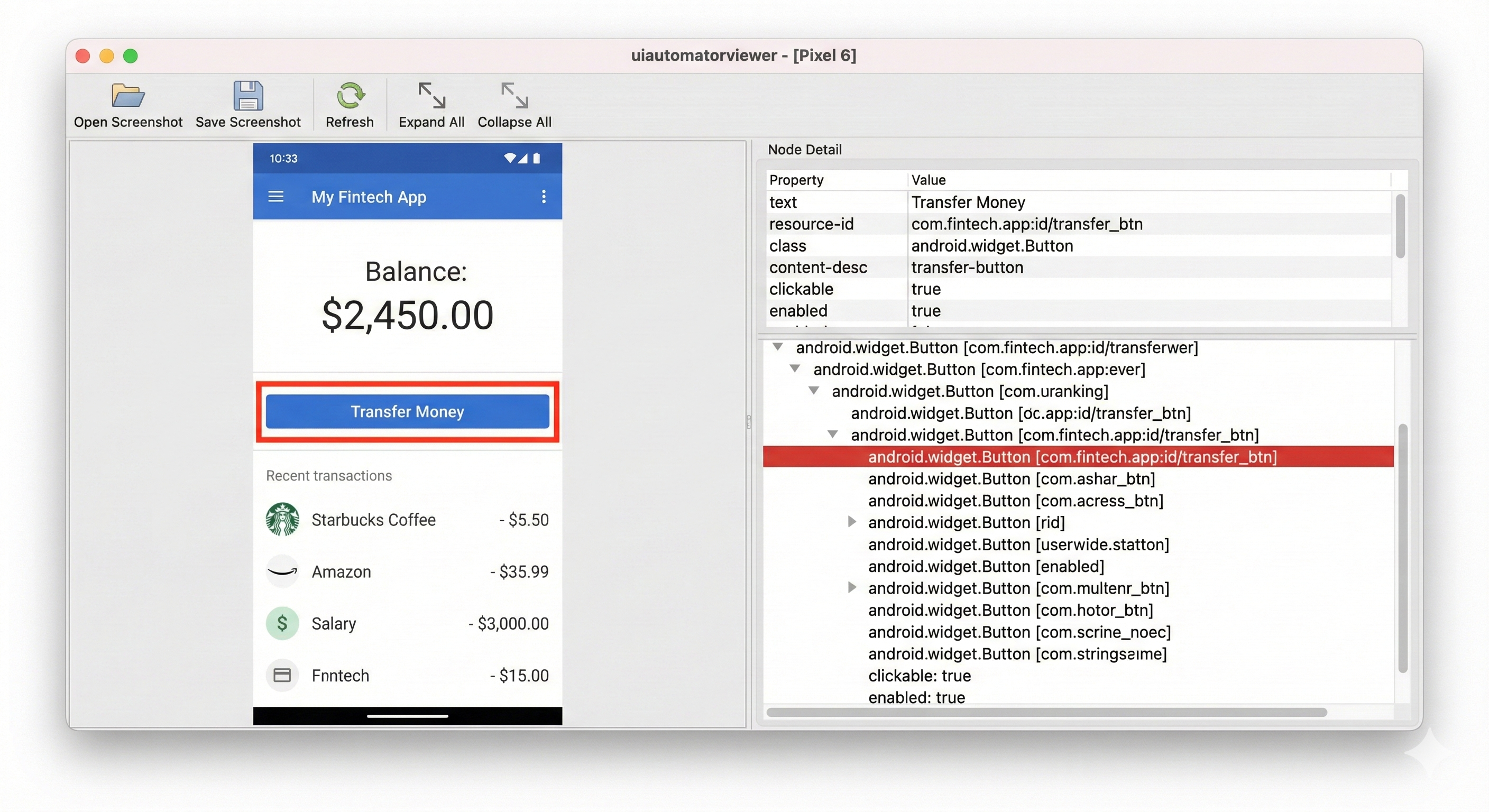
Use uiautomatorviewer to inspect your app's UI hierarchy:
# Start your emulator and open your app
emulator -avd AppiumTest
# Install your app
adb install /path/to/app.apk
# Open the app screen you want to inspect
# Then run uiautomatorviewer
$ANDROID_HOME/tools/bin/uiautomatorviewerThis opens a GUI tool that lets you:
- Click "Device Screenshot" to capture current screen
- Hover over elements to see their properties
- Find
content-desc,resource-id,text, andclassattributes
Appium Android Element Interactions: Tap, Swipe, and Input
Once you find elements, here's how to interact with them:
Tapping Elements
const button = await $('~submit-button');
await button.click();
// Alternative: tap by coordinates
await driver.touchAction({
action: 'tap',
x: 200,
y: 400
});Entering Text
const emailField = await $('~email-input');
await emailField.setValue('user@example.com');
// Clear existing text first
await emailField.clearValue();
await emailField.setValue('newuser@example.com');
// Add to existing text
await emailField.addValue(' additional text');Swiping and Scrolling
// Swipe down to refresh
await driver.touchAction([
{ action: 'press', x: 200, y: 400 },
{ action: 'wait', ms: 500 },
{ action: 'moveTo', x: 200, y: 800 },
'release'
]);
// Scroll to element (UIAutomator method)
await $('android=new UiScrollable(new UiSelector().scrollable(true)).scrollIntoView(new UiSelector().text("Account Settings"))');
// Swipe element (like dismissing a card)
const element = await $('~transaction-card');
await element.touchAction([
{ action: 'press', x: 0, y: 0 },
{ action: 'wait', ms: 100 },
{ action: 'moveTo', x: -300, y: 0 },
'release'
]);Long Press
const element = await $('~transaction-item');
await element.touchAction([
{ action: 'longPress' },
{ action: 'release' }
]);
// Long press with duration
await driver.touchAction([
{ action: 'longPress', x: 200, y: 400 },
{ action: 'wait', ms: 2000 },
'release'
]);Getting Element Text and Attributes
const balanceElement = await $('~account-balance');
// Get displayed text
const balanceText = await balanceElement.getText();
console.log(`Current balance: ${balanceText}`); // "Current balance: $2,450.00"
// Get attribute value
const resourceId = await balanceElement.getAttribute('resource-id');
const isEnabled = await balanceElement.getAttribute('enabled');
// Check if element is displayed
const isVisible = await balanceElement.isDisplayed();
// Check if element exists
const exists = await balanceElement.isExisting();Real-World Example: Mobile Test Automation for Transaction Flows
Here's a realistic test for a money transfer in a fintech app:
describe('Money Transfer Flow', () => {
it('should transfer money between accounts successfully', async () => {
// Login first
await $('~email-input').setValue('user@example.com');
await $('~password-input').setValue('SecurePass123!');
await $('~login-button').click();
// Wait for home screen
await driver.pause(2000);
// Get initial balance
const initialBalanceText = await $('~account-balance').getText();
const initialBalance = parseFloat(initialBalanceText.replace(/[$,]/g, ''));
// Navigate to transfer screen
await $('~transfer-button').click();
await driver.pause(1000);
// Select recipient account
await $('~recipient-dropdown').click();
await $('//*[@text="Savings Account"]').click();
// Enter transfer amount
await $('~amount-input').setValue('100.00');
// Add memo
await $('~memo-input').setValue('Test transfer');
// Review transfer details
await $('~review-button').click();
await driver.pause(500);
// Verify transfer details are correct
const confirmAmount = await $('~confirm-amount').getText();
expect(confirmAmount).toBe('$100.00');
const confirmRecipient = await $('~confirm-recipient').getText();
expect(confirmRecipient).toBe('Savings Account');
// Confirm transfer
await $('~confirm-transfer-button').click();
// Wait for success message
await driver.pause(2000);
const successMessage = await $('~success-message');
expect(await successMessage.isDisplayed()).toBe(true);
// Navigate back to home
await $('~home-button').click();
await driver.pause(1000);
// Verify balance decreased
const newBalanceText = await $('~account-balance').getText();
const newBalance = parseFloat(newBalanceText.replace(/[$,]/g, ''));
expect(newBalance).toBe(initialBalance - 100);
});
it('should reject transfer with insufficient funds', async () => {
// Navigate to transfer screen
await $('~transfer-button').click();
// Select recipient
await $('~recipient-dropdown').click();
await $('//*[@text="Savings Account"]').click();
// Try to transfer more than available balance
await $('~amount-input').setValue('999999.00');
await $('~review-button').click();
// Verify error message appears
await driver.pause(500);
const errorMessage = await $('//*[@text="Insufficient funds"]');
expect(await errorMessage.isDisplayed()).toBe(true);
// Confirm button should be disabled
const confirmButton = await $('~confirm-transfer-button');
const isEnabled = await confirmButton.getAttribute('enabled');
expect(isEnabled).toBe('false');
});
});Handling Android System Dialogs and Permissions
Android apps often trigger system dialogs for permissions. Handle them with UIAutomator:
describe('Permission Handling', () => {
it('should grant camera permission when requested', async () => {
// Trigger camera feature
await $('~scan-check-button').click();
// Wait for permission dialog
await driver.pause(1000);
// Grant permission using UIAutomator selector
const allowButton = await $('android=new UiSelector().text("Allow")');
await allowButton.click();
// Verify camera view is now visible
const cameraView = await $('~camera-preview');
expect(await cameraView.isDisplayed()).toBe(true);
});
it('should handle location permission', async () => {
// Trigger location feature
await $('~find-atm-button').click();
// Wait for permission dialog
await driver.pause(1000);
// Grant precise location
const allowPreciseButton = await $('android=new UiSelector().text("Allow only while using the app")');
await allowPreciseButton.click();
// Verify map loads
const mapView = await $('~atm-map');
expect(await mapView.isDisplayed()).toBe(true);
});
});Appium Test Debugging: Screenshots and Video Recording
Capture screenshots during test execution for debugging:
describe('Screenshot Example', () => {
it('should capture screenshots at key points', async () => {
// Take screenshot before action
await driver.saveScreenshot('./screenshots/before-login.png');
// Perform login
await $('~email-input').setValue('user@example.com');
await $('~password-input').setValue('SecurePass123!');
await $('~login-button').click();
await driver.pause(2000);
// Take screenshot after successful login
await driver.saveScreenshot('./screenshots/after-login.png');
// Take screenshot of specific element
const balanceElement = await $('~account-balance');
await balanceElement.saveScreenshot('./screenshots/balance-element.png');
});
});Record video of test execution:
describe('Video Recording', () => {
before(async () => {
// Start recording
await driver.startRecordingScreen({
videoSize: '1280x720',
bitRate: 3000000
});
});
it('should execute transaction flow', async () => {
// Your test code here
await $('~transfer-button').click();
// ... more test steps
});
after(async () => {
// Stop recording and save
const videoBase64 = await driver.stopRecordingScreen();
const fs = require('fs');
fs.writeFileSync('./recordings/test-execution.mp4', videoBase64, 'base64');
});
});Appium Troubleshooting: 17 Common Android Testing Problems Solved
Quick Navigation - Jump to Your Problem:
- Server Won't Start
- Device Not Detected
- Element Not Found
- Test Timeouts
- App Crashes
- Keyboard Issues
- Flaky Tests
- Can't Install APK
- Slow Tests
- Real Device Issues
- Network Failures
- Version Compatibility
- Deep Links
- Memory Leaks
- Biometric Auth
- Scrolling Issues
- CI/CD Failures
1. Fix: Appium Server Won't Start
Symptoms: Running appium shows error or nothing happens.
Cause: Port 4723 already in use, or Node.js version incompatibility.
Solution:
# Check if port is in use
lsof -i :4723 # macOS/Linux
netstat -ano | findstr :4723 # Windows
# Kill process using port
kill -9 <PID> # macOS/Linux
# Start Appium on different port
appium --port 4725
# Update wdio.conf.js to match
# port: 4725Verify Node.js version:
node --version
# Need v14 or higher for Appium 2.x
# Update if needed (macOS)
brew upgrade node2. Fix: Android Device/Emulator Not Detected by ADB
Symptoms: adb devices shows empty list or "unauthorized".
Cause: ADB server not started, USB debugging disabled, or device not authorized.
Solution:
# Restart ADB server
adb kill-server
adb start-server
# List devices again
adb devices
# If device shows "unauthorized", check device for authorization prompt
# Accept "Allow USB debugging" on your Android deviceFor emulator specifically:
# Check emulator is running
emulator -list-avds
ps aux | grep emulator
# Start emulator if not running
emulator -avd AppiumTest -no-snapshot-load
# Wait 30-60 seconds for full boot
# Then check adb again
adb devices3. Fix: Element Not Found Errors in Appium Tests
Symptoms: Error: Can't call click on element with selector "~login-button" because element wasn't found
Cause: Incorrect selector, element not yet rendered, or timing issue.
Solution:
// Add explicit wait
const loginButton = await $('~login-button');
await loginButton.waitForDisplayed({ timeout: 5000 });
await loginButton.click();
// Or use WebDriverIO's built-in retry
await driver.waitUntil(
async () => {
const button = await $('~login-button');
return await button.isDisplayed();
},
{
timeout: 10000,
timeoutMsg: 'Login button not found after 10 seconds'
}
);Verify selector is correct using uiautomatorviewer. Common mistakes:
// Wrong - missing tilde for accessibility ID
const element = await $('login-button');
// Correct
const element = await $('~login-button');
// Wrong - incorrect XPath quotes
const element = await $("//*[@text='Login']");
// Correct
const element = await $('//*[@text="Login"]');4. Fix: Appium Tests Timeout Waiting for App Launch
Symptoms: Test fails with timeout error before app even opens.
Cause: Wrong appWaitActivity or app takes too long to start.
Solution:
Find correct activity name:
# Install and launch app manually
adb install app.apk
adb shell monkey -p com.yourapp -c android.intent.category.LAUNCHER 1
# Check current activity
adb shell dumpsys window windows | grep -E 'mCurrentFocus'
# Output: mCurrentFocus=Window{abc123 u0 com.yourapp/.activities.SplashActivity}Update config:
capabilities: [{
// ...
'appium:appWaitActivity': 'com.yourapp/.activities.SplashActivity',
'appium:appWaitDuration': 30000, // Wait up to 30 seconds
}]Or disable wait and add manual wait:
capabilities: [{
// ...
'appium:appWaitActivity': '*', // Any activity
}]
// In test
await driver.pause(5000); // Wait for app to fully load5. Fix: Android App Crashes During Test Execution
Symptoms: App suddenly closes, test fails with session error.
Cause: App bug triggered by test, memory issue, or race condition.
Solution:
Get crash logs:
# Capture logcat output during test
adb logcat > logcat-output.txt
# Filter for crashes
adb logcat | grep -i "fatal\|exception\|crash"
# Check specifically for your app
adb logcat | grep "com.yourapp"Add error handling in tests:
try {
await $('~submit-button').click();
await driver.pause(2000);
} catch (error) {
// Capture screenshot before test fails
await driver.saveScreenshot('./screenshots/error-state.png');
// Get app state
const currentActivity = await driver.getCurrentActivity();
console.log('Current activity:', currentActivity);
throw error;
}6. Fix: Keyboard Interferes with Appium Element Interaction
Symptoms: Can't find or click elements when keyboard is open.
Cause: Keyboard overlays the element you're trying to interact with.
Solution:
// Hide keyboard before interacting with elements
await driver.hideKeyboard();
// Or press back button
await driver.pressKeyCode(4); // 4 is Back button keycode
// Wait a moment for keyboard animation
await driver.pause(500);
// Now interact with element
await $('~submit-button').click();For better UX testing, scroll element into view:
// Scroll to make element visible above keyboard
await $('android=new UiScrollable(new UiSelector().scrollable(true)).scrollIntoView(new UiSelector().resourceId("com.app:id/submit_button"))');
await $('~submit-button').click();7. Fix: Flaky Android Tests Due to Animations
Symptoms: Tests pass sometimes, fail other times with "element not clickable" errors.
Cause: Animations haven't completed, or element is mid-transition.
Solution:
Disable animations on emulator (recommended for testing):
# Disable all animations
adb shell settings put global window_animation_scale 0
adb shell settings put global transition_animation_scale 0
adb shell settings put global animator_duration_scale 0
# Re-enable after testing (optional)
adb shell settings put global window_animation_scale 1
adb shell settings put global transition_animation_scale 1
adb shell settings put global animator_duration_scale 1For more strategies on preventing flaky tests, read our comprehensive guide: How to Reduce Test Flakiness: Best Practices and Solutions.
Or wait for element to be clickable:
const button = await $('~transfer-button');
// Wait for element to be clickable (not just displayed)
await button.waitForClickable({ timeout: 5000 });
await button.click();8. Fix: Appium Can't Install APK on Android Device
Symptoms: Error: An unknown server-side error occurred while processing the command. Original error: Error executing adbExec. Stderr: 'Failure [INSTALL_FAILED_UPDATE_INCOMPATIBLE]'
Cause: App with same package name already installed with different signature.
Solution:
# Uninstall existing app
adb uninstall com.yourapp.package
# Or set noReset: false in capabilities to auto-uninstallIn wdio.conf.js:
capabilities: [{
// ...
'appium:noReset': false, // Uninstall app after each session
'appium:fullReset': true, // Also clear app data
}]9. Fix: Slow Appium Test Execution Time
Symptoms: Each test takes 2-3 minutes instead of seconds.
Cause: Implicit waits too long, or inefficient selectors.
Solution:
Optimize wait times:
// In wdio.conf.js
waitforTimeout: 5000, // Reduce from default 10000
// Use explicit waits instead of pause
// Bad
await driver.pause(5000);
// Good
await $('~element').waitForDisplayed({ timeout: 5000 });Use efficient selectors:
// Slow - XPath searches entire hierarchy
const button = await $('//android.widget.Button[@text="Submit"]');
// Fast - direct accessibility ID
const button = await $('~submit-button');
// Fast - resource ID
const button = await $('id=com.app:id/submit_button');Reuse sessions when possible:
// In wdio.conf.js
capabilities: [{
// ...
'appium:noReset': true, // Keep app installed between tests
}]
// Login once in before() hook instead of each test
before(async () => {
await $('~email-input').setValue('user@example.com');
await $('~password-input').setValue('SecurePass123!');
await $('~login-button').click();
await driver.pause(2000);
});10. Fix: Testing on Real Android Device Issues
Symptoms: Emulator works fine, but real device shows "device unauthorized" or doesn't appear.
Cause: USB debugging not enabled, or drivers not installed (Windows).
Solution:
Enable USB debugging on device:
- Settings → About Phone → Tap "Build number" 7 times
- Settings → Developer Options → Enable "USB Debugging"
- Connect device via USB
- Accept "Allow USB debugging" prompt on device
Verify connection:
adb devices
# Should show:
# List of devices attached
# ABC123456789 deviceWindows users need USB drivers:
- Samsung: Install Samsung USB drivers
- Google Pixel: Should work automatically
- Other devices: Install manufacturer's USB drivers
Update capabilities for real device:
capabilities: [{
// ...
'appium:deviceName': 'ABC123456789', // Your device ID from adb devices
'appium:udid': 'ABC123456789', // Same as device name
}]11. Fix: Network Requests Fail During Appium Tests
Symptoms: App shows "No internet connection" during test, even though network is available.
Cause: Emulator doesn't have internet access, or app uses localhost that points to emulator's localhost.
Solution:
Check emulator network:
# From emulator, ping Google
adb shell ping -c 3 google.com
# If fails, restart emulator with network
emulator -avd AppiumTest -dns-server 8.8.8.8For apps connecting to localhost API during development:
# Forward emulator port to host machine
adb reverse tcp:8080 tcp:8080
# Now emulator's localhost:8080 points to host's localhost:8080Or use 10.0.2.2 in app to reach host machine:
// Instead of
const API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080';
// Use
const API_URL = 'http://10.0.2.2:8080'; // Emulator only12. Fix: Tests Fail on Different Android Versions
Symptoms: Test passes on Android 13, fails on Android 11 with "element not found".
Cause: UI element IDs or hierarchy changed between Android versions.
Solution:
Use version-agnostic selectors:
// Instead of hardcoded resource IDs (can change between versions)
const button = await $('id=com.android.permissioncontroller:id/permission_allow_button');
// Use text that's consistent
const button = await $('android=new UiSelector().text("Allow")');
// Or use multiple fallback selectors
async function findPermissionButton() {
try {
return await $('id=com.android.permissioncontroller:id/permission_allow_button');
} catch {
try {
return await $('id=com.android.packageinstaller:id/permission_allow_button');
} catch {
return await $('android=new UiSelector().text("Allow")');
}
}
}
const button = await findPermissionButton();
await button.click();Test against multiple Android versions in parallel:
// In wdio.conf.js
capabilities: [
{
platformName: 'Android',
'appium:platformVersion': '11.0',
'appium:deviceName': 'Android11Emulator',
'appium:app': '/path/to/app.apk'
},
{
platformName: 'Android',
'appium:platformVersion': '13.0',
'appium:deviceName': 'Android13Emulator',
'appium:app': '/path/to/app.apk'
}
]13. Fix: Deep Links and App Links in Appium Android Tests
Symptoms: Need to test deep links like myapp://transfer/123 but don't know how.
Cause: Deep links require special handling in Appium.
Solution:
// Open deep link during test
await driver.execute('mobile: deepLink', {
url: 'myapp://transfer/123',
package: 'com.yourapp.package'
});
// Wait for app to process deep link
await driver.pause(2000);
// Verify you're on correct screen
const transferScreen = await $('~transfer-details-screen');
expect(await transferScreen.isDisplayed()).toBe(true);
// Test app link (HTTPS link that opens app)
await driver.execute('mobile: deepLink', {
url: 'https://yourapp.com/transfer/123',
package: 'com.yourapp.package'
});Alternative using adb:
await driver.execute('mobile: shell', {
command: 'am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "myapp://transfer/123" com.yourapp.package'
});14. Fix: Memory Leaks in Long Appium Test Runs
Symptoms: First few tests pass, then later tests slow down or fail with OutOfMemory errors.
Cause: App or Appium session accumulating memory over multiple tests.
Solution:
Reset app state between tests:
// In wdio.conf.js
afterTest: async function() {
// Clear app data and restart
await driver.reset();
}
// Or terminate and relaunch app
afterTest: async function() {
await driver.terminateApp('com.yourapp.package');
await driver.pause(1000);
await driver.activateApp('com.yourapp.package');
}Limit test suite size:
// Split into smaller suites
// suite1.spec.js - login tests (5-10 tests)
// suite2.spec.js - transfer tests (5-10 tests)
// suite3.spec.js - profile tests (5-10 tests)
// Run separately
npx wdio run wdio.conf.js --spec test/specs/suite1.spec.js15. Fix: Biometric Authentication Testing with Appium
Symptoms: App requires fingerprint/face unlock but emulator doesn't support it.
Cause: Emulator needs biometric feature configured.
Solution:
Enable biometric on emulator:
# Set up fingerprint on running emulator
adb -e emu finger touch 1
# Or enable face unlock via emulator extended controls
# Extended Controls → Fingerprint → Touch the sensorIn your test:
describe('Biometric Login', () => {
it('should authenticate with fingerprint', async () => {
// Trigger biometric prompt
await $('~use-biometric-button').click();
// Wait for biometric dialog
await driver.pause(1000);
// Simulate fingerprint touch
await driver.execute('mobile: fingerprint', { action: 'authenticate' });
// Or using adb
await driver.execute('mobile: shell', {
command: 'adb -e emu finger touch 1'
});
// Wait for authentication
await driver.pause(1000);
// Verify logged in
const homeScreen = await $('~home-screen');
expect(await homeScreen.isDisplayed()).toBe(true);
});
});16. Fix: Can't Scroll to Find Elements in Android Apps
Symptoms: Element exists but not visible on screen, standard selector can't find it.
Cause: Element is below the fold and requires scrolling.
Solution:
// Scroll into view using UIAutomator
await $('android=new UiScrollable(new UiSelector().scrollable(true)).scrollIntoView(new UiSelector().text("Account Settings"))');
// For horizontal scroll
await $('android=new UiScrollable(new UiSelector().scrollable(true).instance(0)).setAsHorizontalList().scrollForward()');
// Scroll to end of list
await $('android=new UiScrollable(new UiSelector().scrollable(true)).scrollToEnd(10)'); // max 10 swipes
// Custom scroll action
await driver.execute('mobile: scrollGesture', {
left: 100,
top: 400,
width: 600,
height: 800,
direction: 'down',
percent: 3.0
});17. Fix: Appium Tests Fail in CI/CD Pipeline
Symptoms: Tests pass locally but fail on Jenkins/GitHub Actions/GitLab CI.
Cause: CI environment doesn't have Android SDK, emulator, or proper configuration.
Solution:
For GitHub Actions, use android-emulator-runner:
name: Android Tests
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: macos-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Java
uses: actions/setup-java@v3
with:
java-version: '11'
distribution: 'adopt'
- name: Set up Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: '18'
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
npm install -g appium
appium driver install uiautomator2
npm install
- name: Run Appium tests
uses: reactivecircus/android-emulator-runner@v2
with:
api-level: 33
target: google_apis
arch: x86_64
profile: pixel_5
script: |
appium &
sleep 10
npx wdio run wdio.conf.jsBest Practices for Maintainable Android Tests
Use Page Object Model for Organized Test Architecture
Organize your tests using Page Object Model (POM) to keep tests maintainable. For a complete guide to implementing POM, check out our article on Page Object Model: Building Maintainable Test Automation.
// pages/LoginPage.js
class LoginPage {
get emailInput() { return $('~email-input'); }
get passwordInput() { return $('~password-input'); }
get loginButton() { return $('~login-button'); }
get errorMessage() { return $('//*[@text="Invalid email or password"]'); }
async login(email, password) {
await this.emailInput.setValue(email);
await this.passwordInput.setValue(password);
await this.loginButton.click();
await driver.pause(2000);
}
async getErrorMessage() {
return await this.errorMessage.getText();
}
}
module.exports = new LoginPage();Use in tests:
// test/specs/login.spec.js
const LoginPage = require('../pages/LoginPage');
const HomePage = require('../pages/HomePage');
describe('Login Tests', () => {
it('should login successfully', async () => {
await LoginPage.login('user@example.com', 'SecurePass123!');
const balance = await HomePage.getBalance();
expect(balance).toContain('$');
});
it('should show error for invalid credentials', async () => {
await LoginPage.login('invalid@example.com', 'wrong');
const error = await LoginPage.getErrorMessage();
expect(error).toBe('Invalid email or password');
});
});Externalize Test Data
Don't hardcode test data in tests:
// testdata/users.json
{
"validUser": {
"email": "user@example.com",
"password": "SecurePass123!"
},
"invalidUser": {
"email": "invalid@example.com",
"password": "wrong"
}
}// test/specs/login.spec.js
const testData = require('../testdata/users.json');
describe('Login Tests', () => {
it('should login successfully', async () => {
await LoginPage.login(
testData.validUser.email,
testData.validUser.password
);
expect(await HomePage.isDisplayed()).toBe(true);
});
});Implement Custom Waits
Create reusable wait functions:
// utils/waits.js
class Waits {
async waitForElementAndClick(selector, timeout = 10000) {
const element = await $(selector);
await element.waitForClickable({ timeout });
await element.click();
}
async waitForTextAndVerify(selector, expectedText, timeout = 10000) {
await driver.waitUntil(
async () => {
const element = await $(selector);
const text = await element.getText();
return text === expectedText;
},
{
timeout,
timeoutMsg: `Expected text "${expectedText}" not found after ${timeout}ms`
}
);
}
async waitForElementToDisappear(selector, timeout = 10000) {
await driver.waitUntil(
async () => {
try {
const element = await $(selector);
return !(await element.isDisplayed());
} catch {
return true; // Element doesn't exist anymore
}
},
{
timeout,
timeoutMsg: `Element still visible after ${timeout}ms`
}
);
}
}
module.exports = new Waits();Add Comprehensive Logging
Log key actions and states:
// utils/logger.js
class Logger {
info(message) {
console.log(`[INFO] ${new Date().toISOString()} - ${message}`);
}
async logAction(action, selector) {
const timestamp = new Date().toISOString();
console.log(`[ACTION] ${timestamp} - ${action} on ${selector}`);
}
async logAppState() {
const activity = await driver.getCurrentActivity();
const packageName = await driver.getCurrentPackage();
console.log(`[STATE] Current: ${packageName}/${activity}`);
}
}
module.exports = new Logger();Use in tests:
const logger = require('../utils/logger');
describe('Transfer Test', () => {
it('should complete transfer', async () => {
logger.info('Starting transfer test');
await logger.logAction('click', 'transfer-button');
await $('~transfer-button').click();
await logger.logAppState();
// ... rest of test
});
});Frequently Asked Questions About Appium Android Testing
Appium is an open-source test automation framework used for testing mobile applications on Android and iOS. It allows developers to write automated tests that simulate user interactions like tapping buttons, entering text, and navigating through apps. Appium supports testing native apps, hybrid apps, and mobile web browsers without requiring changes to the app's source code.
Yes, Appium is excellent for Android testing, especially when you need cross-platform coverage (Android and iOS) or want to test the production APK without modifications. It uses UIAutomator2 for Android automation, supports multiple programming languages (JavaScript, Python, Java), and works with real devices and emulators. However, for Android-only projects requiring maximum speed, Espresso might be faster.
1. Install Java JDK 8 or higher
2. Install Node.js and npm
3. Install Android Studio and Android SDK
4. Set ANDROID_HOME environment variable
5. Install Appium globally:
npm install -g appium6. Install UIAutomator2 driver:
appium driver install uiautomator27. Create an Android Virtual Device (AVD)
8. Install WebDriverIO and configure capabilities
9. Start Appium server and run your first test
The complete setup takes 30-45 minutes for first-time installation.
Appium is specifically designed for mobile app testing (Android and iOS), while Selenium is for web browser automation. Appium extends the WebDriver protocol to support mobile platforms and uses mobile-specific drivers (UIAutomator2 for Android, XCUITest for iOS). Selenium tests run in web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari) and cannot test native mobile apps. However, both use similar APIs, so developers familiar with Selenium can quickly learn Appium.
Developers with programming experience can learn Appium basics in 1-2 weeks. Setting up the environment takes 1-2 days, understanding element locators and interactions takes 2-3 days, and mastering troubleshooting common issues takes 1-2 weeks of practice. Complete proficiency, including Page Object Model, CI/CD integration, and handling complex scenarios, typically requires 1-2 months of hands-on experience.
Yes, Appium is designed for cross-platform mobile testing. You can write test logic once and run it on both Android and iOS by configuring different capabilities for each platform. Android uses the UIAutomator2 driver, while iOS uses the XCUITest driver. About 70-80% of test code can be shared between platforms, with platform-specific differences mainly in capabilities configuration and some element selectors.
Yes, Appium is completely free and open-source under the Apache 2.0 license. There are no licensing fees, user limits, or premium features. All functionality is available for free. However, you may incur costs for cloud device testing services (like BrowserStack or Sauce Labs) if you choose to use them instead of local devices/emulators.
Appium supports multiple programming languages including JavaScript (Node.js), Python, Java, Ruby, C#, and PHP. This article uses JavaScript with WebDriverIO, which is popular for its modern async/await syntax and active community. Choose the language your team is most comfortable with–Appium's functionality is the same across all supported languages.
- Accessibility ID (content-desc):
$('~login-button') - Most reliable- Resource ID:
$('id=com.app:id/button') - Fast and reliable- XPath:
$('//android.widget.Button[@text="Login"]') - Flexible but slower- UIAutomator selector:
$('android=new UiSelector().text("Login")') - Most powerful for AndroidUse uiautomatorviewer tool to inspect your app's UI hierarchy and find element properties.
1. Timing issues - Add explicit waits instead of fixed pauses
2. Animations not completing - Disable animations on emulators
3. Network latency - Mock API responses for consistent test data
4. Element selectors changing - Use stable identifiers like accessibility IDs
5. Resource constraints - Ensure adequate RAM and CPU for emulators
6. Different Android versions - Test against multiple versions to catch platform-specific issues
For detailed solutions, see the "Appium Troubleshooting" section above.
Conclusion
You now have everything needed to test Android apps with Appium. You've set up Java, Android SDK, Appium Server, and WebDriverIO. You've written tests for login, transfers, and complex flows. You know how to find elements, handle permissions, and troubleshoot 17 common problems.
The key to successful Appium testing isn't just writing tests–it's writing maintainable tests. Use Page Object Model. Externalize test data. Add proper waits instead of sleeps. Log your actions. Test on multiple Android versions. Run tests in CI/CD using continuous integration mobile testing practices to ensure comprehensive Android test coverage.
Appium gives you the foundation for mobile test automation. Whether you're testing a fintech app, food delivery app, or any Android application, these Android testing best practices will help you catch bugs before users do.
Next steps:
- Set up your first test suite using the examples in this guide
- Configure CI/CD to run tests on every commit
- Expand Android test coverage to critical user journeys
- Consider advanced topics like parallel execution and cloud device testing
For teams looking to streamline their entire QA workflow, explore our AI for QA: A Complete Guide to AI Test Automation to see how AI can enhance your mobile app quality assurance process.
Happy testing!
